python流程控制
750字约3分钟
2024-09-29
条件判断
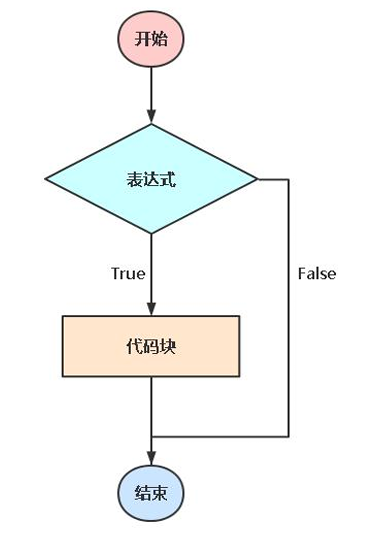
语法:
if <表达式>:
<代码块>
elif <表达式>:
<代码块>
else:
<代码块>条件判断:单分支
示例:判断是否成年
age = int(input("请输入你的年龄: "))
if age > 18:
print("恭喜,你已经成年!")
else:
print("抱歉,你还未成年!")
简写,也成三目表达式: "恭喜,你已经成年!" if age > 18 else "抱歉,你还未成年!"条件判断:多分支
示例:根据人的年龄段划分
age = int(input("请输入你的年龄: "))
if age < 7 :
print("儿童")
elif age >= 7 and age < 17:
print("少年")
elif age >= 18 and age < 40:
print("青年")
elif age >= 41 and age < 48:
print("壮年")
else:
print("老年")循环语句
在了解编程中的“循环”之前,先试想下这个场景: 在阳台种花,准备种4颗种子,开始逐个挖坑,放一颗种子。

每一颗种子操作都是相同的,如果我们用一步将6颗 种子重复种下的行为表示出来呢?
for n in range(1,5):
print("开始种花第%s次" %n)循环的作用在于将一段代码重复执行多次。
Python中实现循环常用有两个语句:for、while
for语句
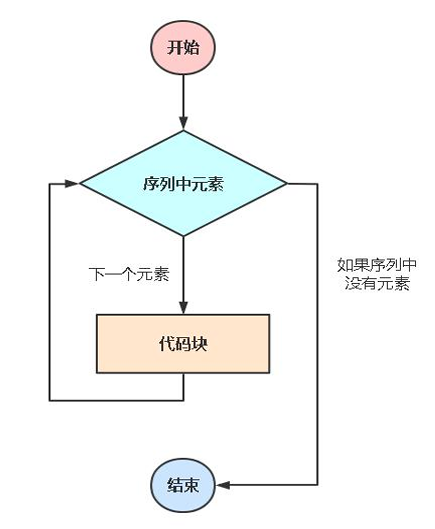
for语句:一般用于遍历数据类型的元素进行处理,例如字符串、列表。
语法:
for <变量> in <序列>:
<代码块>示例1:遍历字符串
s = "123456"
for i in s:
print(i)示例2:遍历列表
computer = ["主机","显示器","鼠标","键盘"]
for i in computer:
print(i,len(i))示例3:遍历字典
computer = {"主机":5000,"显示器":1000,"鼠标":60,"键盘":150}
for i in computer.items():
print(i)
print("名称: %s\t价格: %s" % (i[0],i[1]))示例4:嵌套循环
s1 = "123456"
s2 = "456789"
for i in s1:
for x in s2:
if i == x:
print(i)range()内建函数:动态生成数字序列,例如range(1,6),结果类似列表[1,2,3,4,5,6]
示例:生成0-4序列
for i in range(5):
print(i)while语句
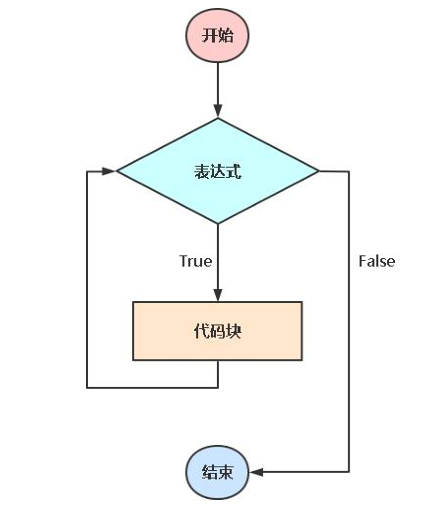
while语句:在某条件下循环执行一段代码,即重复相同的任务。
语法:
while <表达式>:
<代码块>示例1:当条件满足时停止循环
count = 0
while count < 5:
print(count)
count += 1示例2:死循环
count = 0
while True:
print(count)
count += 1continue与break语句
continue 当满足条件时,跳出本次循环
break 当满足条件时,跳出所有循环
注:只有在for、while循环语句中才有效。
示例1:continue
for n in range(1,6):
if n == 3:
continue
else:
print(n)示例2:break
for n in range(1,6):
if n == 3:
break
else:
print(n)综合案例:用户登录,三次错误机会
示例:
count = 0
while True:
if count < 3:
username = input('请输入你的用户名:').strip()
if len(username) == 0:
print('用户名不能为空')
continue
elif username == 'azhe':
print('登录成功')
break
else:
print('输入错误,请重新输入')
count += 1
else:
print('输入错误次数过多,请稍候输入')
break